Three possibilities come to mind:
Is there an evolutionary purpose?
Does it arise as a consequence of our mental activities, a sort of side effect of our thinking?
Is it given a priori (something we have to think in order to think at all)?
EDIT: Thanks for all the responses! Just one thing I saw come up a few times I’d like to address: a lot of people are asking ‘Why assume this?’ The answer is: it’s purely rhetorical! That said, I’m happy with a well thought-out ‘I dispute the premiss’ answer.
Confabulation.
Look at split-brain patients: divide the corpus callosum down the middle, and you effectively have two separate brains that don’t communicate. Tell the half without the speech centre to perform some random task, then ask the other one why they did that - and they will flat-out make up some plausible sounding reason.
And the thing is, they haven’t the slightest idea that it isn’t true. To them, it feels exactly like freely choosing to do it, for those made up reasons.
Bits of our brains make us do stuff for their own reasons, and we just make shit up to explain it after the fact. We invent the memory of choosing, about a quarter of a second after we’ve primed our muscles to carry out the choice.
I think a chunk of this comes down to our need to model the thoughts of others (incredibly useful for social animals) - we make everyone out to be these monolithic executive units so that we can predict their actions, and we make ourselves out to be the same so we can slot ourselves into that same reasoning.
Also it would be a bit fucking terrifying to just constantly get surprised by your own actions, blown around like a leaf on the wind without a clue what’s going on, so I think another chunk of it is just larping this “I” person who has a coherent narrative behind it all, to protect your own sanity.
We invent the memory of choosing, about a quarter of a second after we’ve primed our muscles to carry out the choice.
Where can I read more about this?
There was a relevant post on Lemmy the other day:
The origin and nature of existence is an epistemological black hole that some people like to plug with “a
wizardgod did it”.The sensation of free will is an emergent property of a lack of awareness of the big stuff, the small stuff, the long stuff, and the short stuff.
I like to look at the illusion of free will as if you’re falling down a pit. You can try to flap your arms or swim, and maybe move yourself a little bit, but at the end, you’re still falling down.
Warning, I came up with this while very high one time, lol, but it’s kind of stuck with me:
Consciousness is a 4-dimensional construct living in a 3-dimensional world. What we experience as the passage of time is just our consciousness traveling/falling along the surface of the 4-dimensional plane/shape that defines our existence.
Feel free to poke all the holes you want in that. lol
There is an old Taoist story about two people floating down a river. One has already decided where he wants the river to take him and is constantly swimming against the current to try to get there, the other just floats along taking in the sights.
They both end up wherever the river takes them, and they both went through the same obstacles and rapids, but when asked how the trip was, one of them is complaining about the whole trip being frustrating and exhausting, while the other had a pleasant time and tells you all about the amazing things they saw on the way.
I love that!
Really illustrates the saying, “go with the flow,” too.
This is basically a spacetime worldline, which is one of those terms that sounds like scifi technobabble even though it’s an actual concept
Couldn’t it also be argued that our lack of awareness of the big stuff also leaves open the possibility of free will?
On a sufficiently large billiards table, it does become hard to prove that some balls don’t spontaneously sink themselves.
That is a clever point but I think it also overly simplifies the nature of reality to such a point that it’s not likely to change any minds.
Here’s my take: the answer is emergent phenomena. We live in a very complex system and in complex systems there are interactions that can only be predicted using systems of equal or higher complexity. So even in case everything is predetermined, it would still be unpredictable and therefore your decisions are basically still up to you and the complex interactions in your brain.
I think this is probably it. I think this argument is strongly related to the idea of consciousness as an emergent property of sensory experience. I find it simple to imagine the idea of a body with no will or no consciousness (i.e., a philosophical zombie). But I find it very difficult, almost impossible, in fact, to imagine a consciousness with no will, even if it’s only the will to think a given thought.
Do we have free will to think a given thought? All of my thoughts just suddenly appear in my mind or are connected to previous thoughts that suddenly appeared in my mind.
I mean, if I said to you, ‘Calculate 13x16’ (or some other sum you don’t know off the top of your head) you could either do it or not do it. That would be a willed choice, whether or not you knew the answer.
My thoughts would be presented based the fact that you’ve asked me to calculate something. At that point, past experiences would guide my path forward. If I felt like doing math, I may do it, if I had poor childhood experiences in math class, I probably wouldn’t. At the end of the day, it’s all based on history or current questions/feelings. In every scenario my thoughts are presented to me. To prove it, ask yourself what your next thought will be. If you’re honest with yourself, you’ll see you can’t answer that question and when you try and force a thought direction, that direction itself is based on your knowledge from the past and that thought was also presented to you.
It’s wild because it absolutely feels like we have free will, but it sure doesn’t look like it. 🤷♂️
This is the problem of original intentionality. There are studies on it, for instance they found that with an mri they can detect when you have come to a decision before your conscious mind realizes you have. Some processes in our brain are outside of our control, because the brain is not just the neocortex but also includes tens of other structures that evolved separately with specific hard-coded purposes, but that doesn’t mean they are not working as a team. I think in any case you are still reaponsible for the decisions you take.
exactly. that for me is in fact the definition of free will
actually this is the definition that first came up on a search
“the power of acting without the constraint of necessity or fate; the ability to act at one’s own discretion”
so yeah we do have free will. the rest is philosophical masturbation
You can also find the definition of magic or telekinesis, but that doesn’t mean we have them, and not all philosophical question are just “masturbation”. It is an interesting question. It is worth taking free will at least axiomatically as our perception of that freedom even if it is truly deterministic.
If you throw a pair of dice, do they still have to roll if their final positions are predetermined from the point that you let go?
One view is that even a deterministic mind still must execute. An illusion of the capacity to choose between multiple options might be necessary to considering those options which leads to the unavoidable conclusion.
Dice do not choose where they roll.
They also do not pretend choosing, or tell themselves any bullshit…
A better question is, is there any difference between the illusion of free will and actual free will. Is there some experiment you could conduct to tell the difference?
Depends, who’s choosing the experiment?
If it’s the illusion of free will then whoever constructed it most likely made sure we wouldn’t have access to those kinds of experiments, or we wouldn’t think of or choose to do them.
Why assume that an illusion must have a constructor?
Our brains cannot store all the experiences we ever make. It rather only stores ‘hunches’ (via many weightings of neurons). In particular, it also mixes multiple experiences together to reinforce such hunches.
This means that despite there being causal reasons why you might e.g. feel uneasy around big dogs, your brain will likely only reproduce a hunch, a gut feeling of fear.
And then because you don’t remember the concrete causal reasons, it feels like a decision to follow your hunch to get the hell out of there.
This feeling of making a decision is made even stronger, because there isn’t just the big-dog-bad-hunch, but also the don’t-show-fear-to-big-dog-hunch and the I’m-in-a-social-situation-and-it-would-be-rude-to-leave-hunch and many others.There is just an insane amount of past experiences and present sensory input, which makes it impossible to trace back why you would decide a certain way. This gives the illusion of there being no reasons, of free will.
Maybe look up “compatibilism”. It’s a philosophy proposing that both exist.
TIL!
I just made up my own term for it in another post :)
You’re conscious of the decisions you make. Sure they’re the result of a million different variables, chemicles, memories, and predetermined traits, but some of that is active. You are making the choice. Whether you could have made a different one or not doesn’t affect what the choice feels like
Honorary mention, Kurtzgesagt/In a Nutshell https://youtu.be/UebSfjmQNvs?feature=shared
The most accurate answer is: We don’t know.
But there are pieces of scientific evidence that suggest our sense of free will is just another perception process that happens in our brains. Specifically I’m thinking about people who have problems in their brain that make them feel like they AREN’T the one controlling what they do. For example people suffering from derealization - https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/depersonalization-derealization-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20352911
EDIT
As to why our brains have a process that gives us a perception of free will, that’s a much harder question that i think science currently only has conjecture on. If i had to guess I’d guess that either there’s an evolutionary advantage to it, or it’s an emergent property that arises from all the parts of the brain being connected in the way they are
For the same reason that I feel like I’m still right now, while I’m actually spinning and hurtling through space at incredible speed.
ludicrous speed
I forget which philosopher said this but he said something along the lines of if you have the desire and the capacity for an action you do, then deterministic or not, you chose that action. If the tide pulls me where I was already swimming, I still chose to swim there, even if some other force took me half of the way.
But where does your desire and capacity to do that thing come from? It arises from the physical arrangement of neurons/hormones/etc. in your brain and body
Why are you separating “you” from the choices your physical self is making?
I’m not. Did you reply to the correct comment?
Just going to throw out a really good read: Determined by Robert Sapolky. (Behave is also really good.)
He doesn’t really convince me of the core thesis that free will doesn’t exist, or that some of his proposed changes to the legal system to “recognize the absence of free will” in the second half are good courses of action, but he does do a great job of demonstrating what makes us tick from a variety of lenses, how much environmental factors play a role in behavior, and generally arguing to approach people with more empathy and recognition that we might be more like them in a similar situation than we think.
(It is heavy. It’s long and goes into some depth on different fields. But he lays out the main ideas you need to know and doesn’t assume that much knowledge, just a will to learn.)
Behave is incredible.
I read a fucking lot of books about what makes us tick. Behave is (tied for) my favorite. He does actually hint down the determinism path a little in behave, but he goes all in on Determined.
I would still probably generally recommend Behave over Determined, but Determined is directly relevant to the OP.
I have heard somewhere that some people seemed to believe that behind each human’s actions, there is some kind of “daemon” that is invisible, but moving the humans like puppets.
This is conceptualized in the theater mask, through which one can speak.
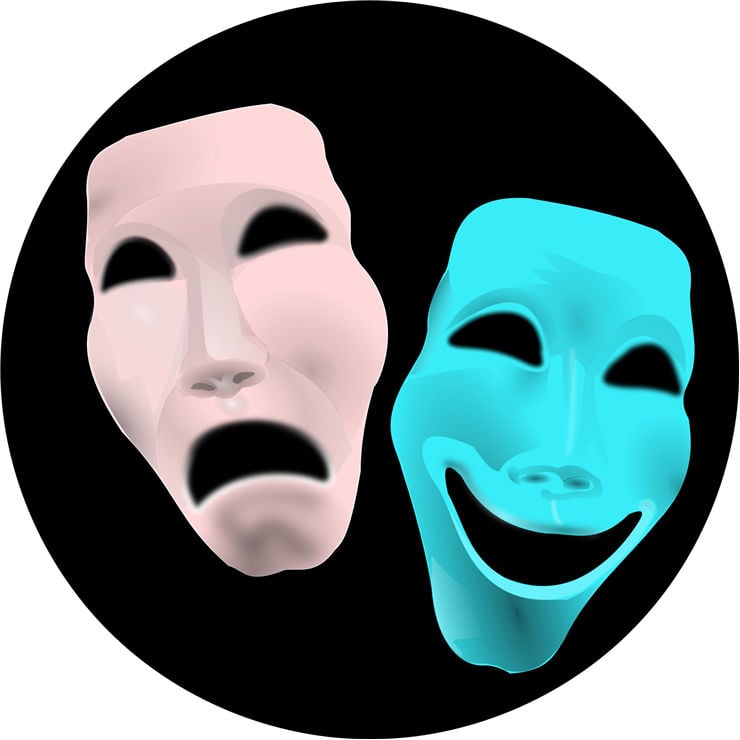

The daemon speaks through the human as a theater actor would speak through a mask. (The latin word for that mask is “persona” (literally “sound-through”) and that’s why we call a person a person today (because they are controlled by a daemon who speaks through them)).
My deamon is now telling you this theory is convoluted and stupid.
I personally think the debate over the existence of Free Will is simply an extraordinary debate over semantics.
If you look at a human being from its basic biological and cellular makeup, a human being is a walking bundle of competing desires that appears to present itself as a single cohesive corporate entity.
The people who are against the concept of free will say that because you have innate desires for food sex and entertainment, that you have no choice to not act upon those in a desires and therefore any delusion that you carry about the choices that you make being done of an entirely unencumbered and Free Will are false.
Then there are people who say that Free Will doesn’t exist for religious purposes, that God is an all-knowing creature who knows the beginning and the end and everything in between and so you cannot make a choice that he or she or it does not already know that you will make and therefore your choices are not free.
The people who say Free Will does exist on a biological level will point to people who choose to self-immolate or to starve themselves to death in protest of a spiritual or psychological issue, valuing the ideals that life has imprinted upon them over the biological necessities of continuing to live.
The people who say Free Will does exist on a spiritual level say many things, such as we carry a spark of the Divine in us and therefore we are as little gods ourselves, capable of creating and destroying in roughly the same proportional magnitude as the greater gods above are, or they say that since we have the ability to make choices and we are judged by those choices than our choices must be free otherwise judgment is meaningless.
I personally tend to lean into the Free Will side, while understanding simultaneously that sometimes there are exigencies that induce us to choose one option over another on a more likely than not basis, or to phrase it another way, our will is as free as we choose it to be.
The people who are against the concept of free will say that because you have innate desires for food sex and entertainment, that you have no choice to not act upon those in a desires and therefore any delusion that you carry about the choices that you make being done of an entirely unencumbered and Free Will are false.
That’s not the argument against free will. The argument is just that there’s a physical process to every thought in your head. When you think of a tree, inside your brain a specific pattern of neurons and chemical messengers activate which is what creates the thought of a tree.
When you’re consciously deciding whether to eat a donut or a salad, a specific pattern of neurons and chemical messengers are the mechanism by which that decision process is occurring. The pattern of neurons and chemical messengers happening in your brain is the physical mechanism that is performing the decision making process.
There are no thoughts outside of the ones generated by your neurons and chemical messengers. The pattern of neurons and chemical messengers IS the thought that you’re thinking. Your brain (and the thoughts that occur within it) is a physical object that obeys the laws of nature, the same as all physical objects do.
I think you’ve mischaracterized the arguments of the “no free will” camp, or at least omitted a major argument. You may find this interesting https://youtu.be/eELfSwqJNKU












